| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Density | 5 x 1022 cm-3 5 x 1028 m-3 |
| Atomic Weight | 28.09 |
| Density (ρ) | 2.328 g cm-3 2328 kg m-3 |
| Energy Bandgap (EG) | 1.1242 eV |
| Intrinsic Carrier Concentration (ni) at 300K* | 1 x 1010 cm-3 1 x 1016 m-3 |
| Intrinsic Carrier Concentration (ni) at 25°C* | 8.6 x 109 cm-3 8.6 x 1015 m-3 |
| Lattice Constant | 0.543095 nm |
| Melting Point | 1415 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.5 Wcm-1K-1 150 Wm-1K-1 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 2.6 x 10-6 K-1 |
| Effective Density of States in the Conduction Band (NC) | 3 x 1019 cm-3 3 x 1025 m-3 |
| Effective Density of States in the Valence Band (NV) | 1 x 1019 cm-3 1 x 1025 m-3 |
| Relative Permittivity (εr) | 11.7 |
| Electron Affinity | 4.05 eV |
| Electron Diffusion Coefficient (De) | kT/q µe |
| Hole Diffusion Coefficient (Dh) | kT/q µh |
* updated values given in 1 2.
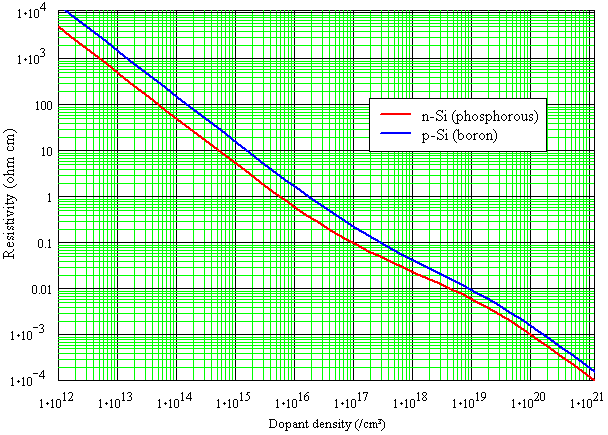
Properties of Silicon as a Function of Doping (300 K)
Carrier mobility is a function of carrier type and doping level. The values calculated here use the same formula as PC1D to fit values given in 3 and 45 6. Lifetime as a function of doping is given on bulk lifetime.
- 1. , “Improved value for the silicon intrinsic carrier concentration at 300 K”, Applied Physics Letters, vol. 57, p. 255, 1990.
- 2. , “Improved value for the silicon intrinsic carrier concentration from 275 to 375 K”, Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 70, pp. 846-854, 1991.
- 3. , “Minority-carrier transport parameters in n-type silicon”, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 37, pp. 1314 - 1322, 1990.
- 4. , “Resistivity-Dopant Density Relationship for Boron-Doped Silicon”, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, vol. 127, pp. 2291-2294, 1980.
- 5. , “Resistivity-Dopant Density Relationship for Phosphorus-Doped Silicon”, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, vol. 127, pp. 1807-1812, 1980.
- 6. “The Relationship Between Resistivity and Dopant Density for Phosphorus- and Boron-Doped Silicon”. U.S. Department of Commerce National Bureau of Standards, 1981.